
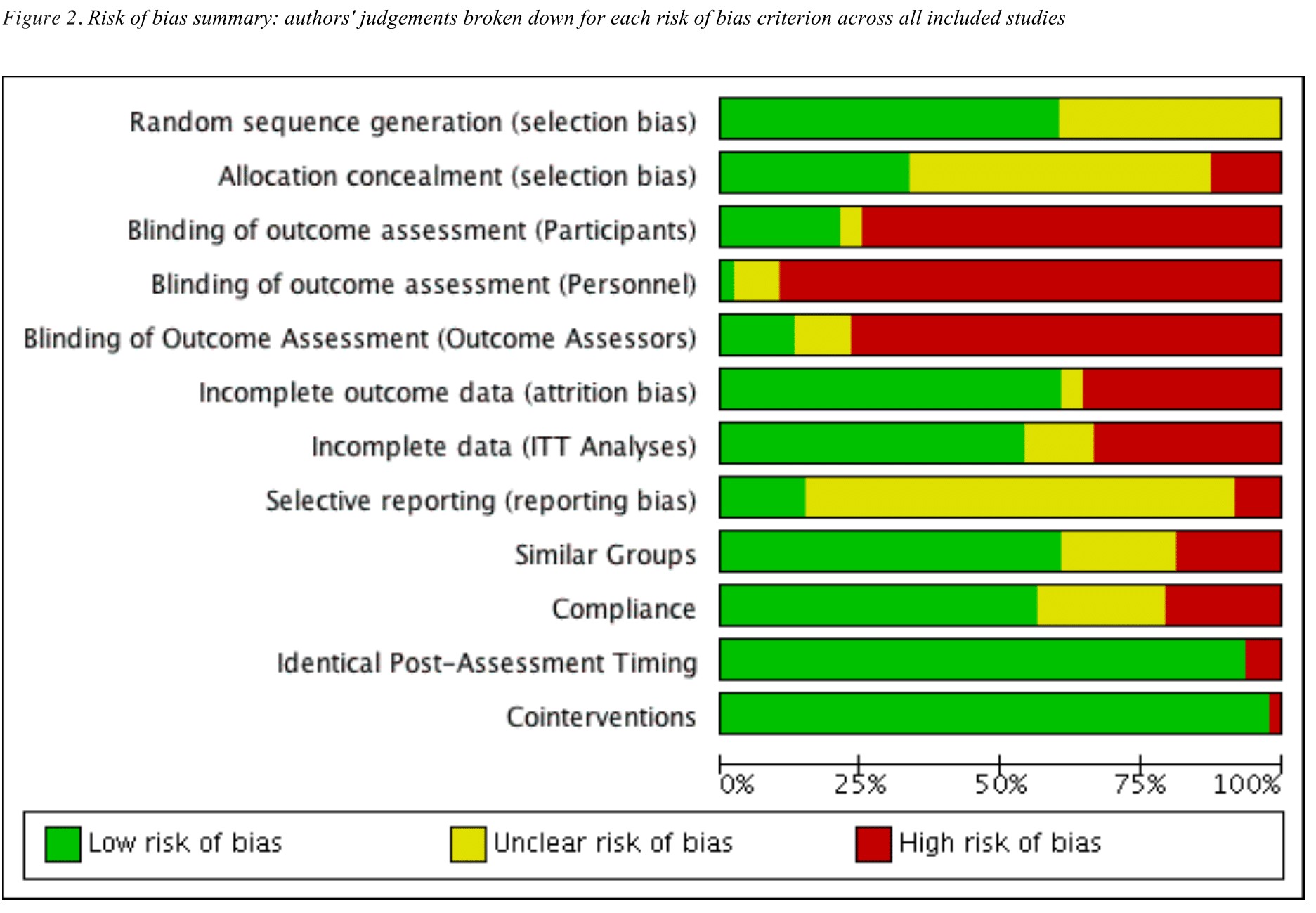

In this systematic review, eligible trials were identified via searches of databases (PubMed, Allied and Complementary Medicine, EMBASE, PEDro, Science Citation Index Expanded, CINAHL, The Cochrane Library, SPORTDiscus) from citation tracking and hand-searching. This study aims to systematically examine the relationship between individual components of the exercise intervention in cardiac rehabilitation (such as intensity and frequency) and clinical outcomes for people with coronary heart disease. It is unknown whether variations in individual components of these exercise interventions provide different relative contributions to overall clinical outcomes. Nephrology © 2012 Asian Pacific Society of Nephrology.While the clinical benefits of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation are well established, there is extensive variation in the interventions used within these trials. Further, this meta-analysis may provide important clues for animal experiments even for human clinical trials in MSC studies. MSCs might get obvious effect in the early stage of renal injuries after arterial delivery. The present meta-analysis confirmed that MSC therapy could improve impaired renal function. Subgroup analysis showed there tended to be greater reduction in Scr with higher MSC number (>10(6)), the renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) model, and late administration (>1 day) after injury. By exploratory multivariable meta-regression, significant influence factors of Scr reduction were the time point of Scr measurement (early measurement showed greater reduction than the late (P = 0.005)) and the route of MSC delivery (arterial delivery of MSCs caused greater reduction in elevated Scr, when compared with the intra-renal delivery and intravenous injection (P = 0.040)).
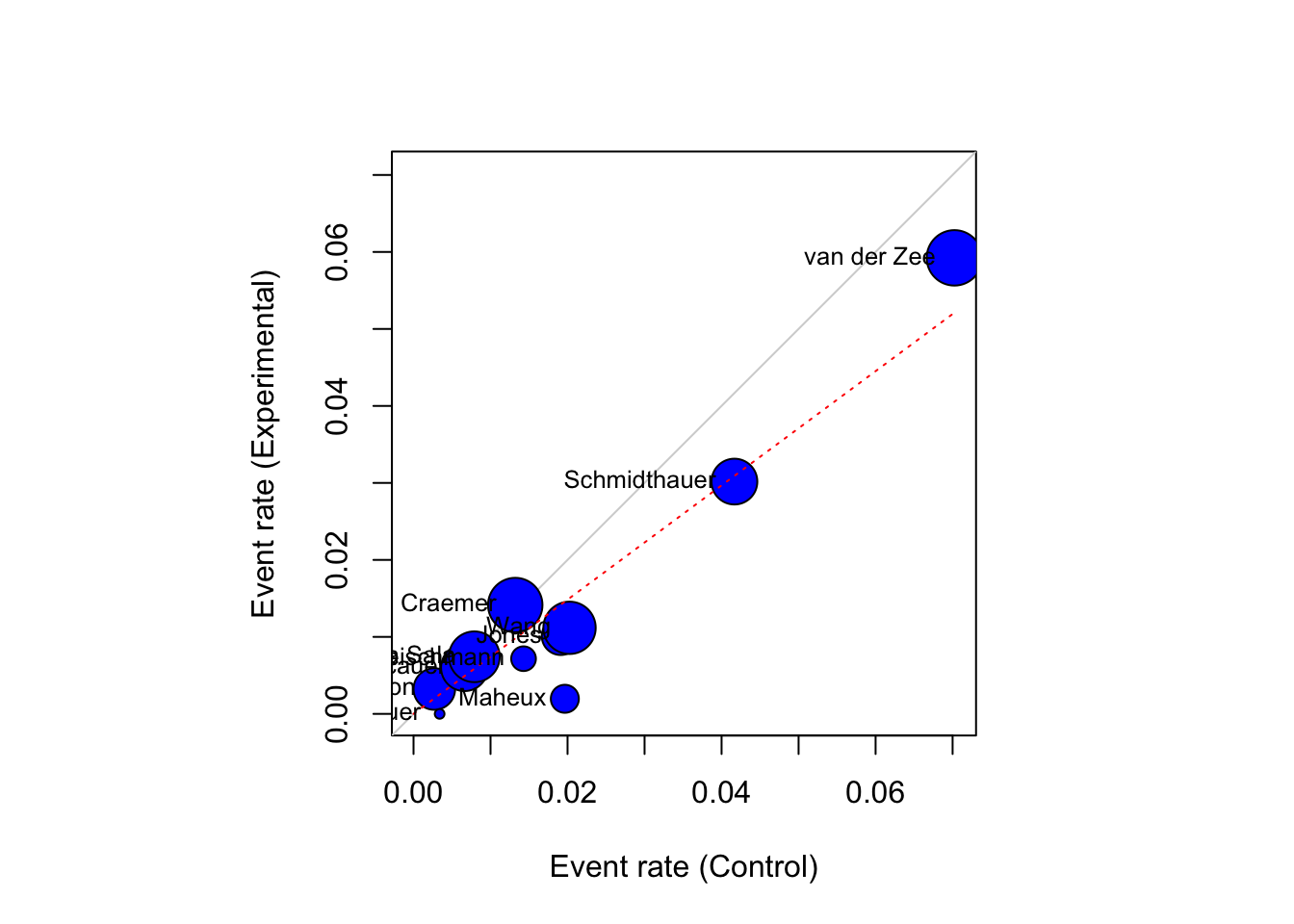
Pooled analysis showed elevated serum creatinine (Scr) reduction in the animal models of renal failure following MSC therapy. Heterogeneity and publication bias across the studies were also explored. Pooled analysis and multivariable meta-regression were calculated by random effects models.

All data were analyzed by RevMan 5.1 and SPSS 17.0. These, were indexed from PubMed and Embase databases. The meta-analysis of recent small animal experiments of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSC) therapy for impaired kidney could provide significant clues to design large animal experiments as well as human clinical trials.Ī total of 21 studies was analyzed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
